BY BRENDAN GRIFFIN AND GARY WARNER
Threat actors have demonstrated that despite the past two years’ explosion in new ransomware varieties, ransomware developers still believe that the market has not reached the point of saturation. Examples of encryption ransomware like Sage have made notable appearances on the phishing threat landscape in the early days of 2017, continuing the ransomware trend from 2016.
The first Sage delivery emails used a sexually explicit email to tempt potential victims into opening an attachment named “sindy_hot_2016_sex_party_in_the_club.zip”. This led to a malware infection from the embedded exe of the same name.
The Sage ransom payment sites used in this campaign are based on TOR address 7gie6ffnkrjykggd[.com and rzunt3u2[.]com, were provided by the threat actor to facilitate access to the payment sites. The command and control host for this campaign was on the Tor address mbfce24rgn65bx3g[.]onion and also resolved using rzunt3u2[.]com and er29sl[.]com as gateways.
Following this early distribution, threat actors moved toward the mainstream in a major way. The phishing email subjects used random numbers to help elude some basic filters and leveraged business-related themes rather than explicit or racy narratives. The body of these emails explained that a financial transaction had been rejected and claimed that details about the failure could be found an attached document.
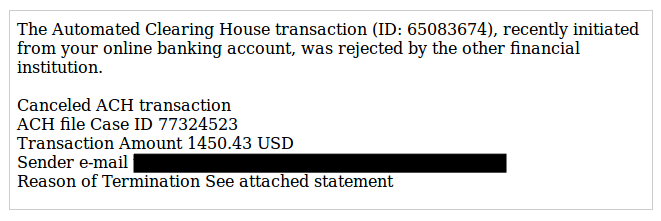
A second variant indicated a that the deposit of a refund had been failed after an order had been canceled.

In this more polished campaign, the .zip file (named “document_1.zip”) contained a JavaScript application which, when run, facilitated the download of a Windows executable representing the Sage Ransomware to be downloaded. In this case, the payload binary was retrieved from the domain affections[.]top, however the payment gateway’s Tor site, as well as the unusual Tor2Web gateway addresses on er29sl[.]com and rzunt3u2[.]com remained the same.
Beginning on January 26th, email narratives and metadata used in these emails began to evidence similarity to phishing campaigns used to deliver the still-persistent Locky ransomware, however the January 26th malware behavior was in every way identical to the previous day’s campaign.
The most interesting finding was the reuse of affections[.]top as part of the delivery process for another ransomware. Locky, one of the flagships of the ransomware market, was delivered as a payload from this domain on Monday, January 30. This connection pushes the narrative forward in yet another way as the Locky distribution in question was yet another example of that ransomware being paired with the Kovter trojan—a trend discussed in Paul Burbage’s post from January 16. This also serves to counter some of the claims that have been made about Locky “missing” from the threat landscape by showing that some threat actors, who choose a different set of tactics, techniques, and procedures, are continuing to deliver this ransomware utility.
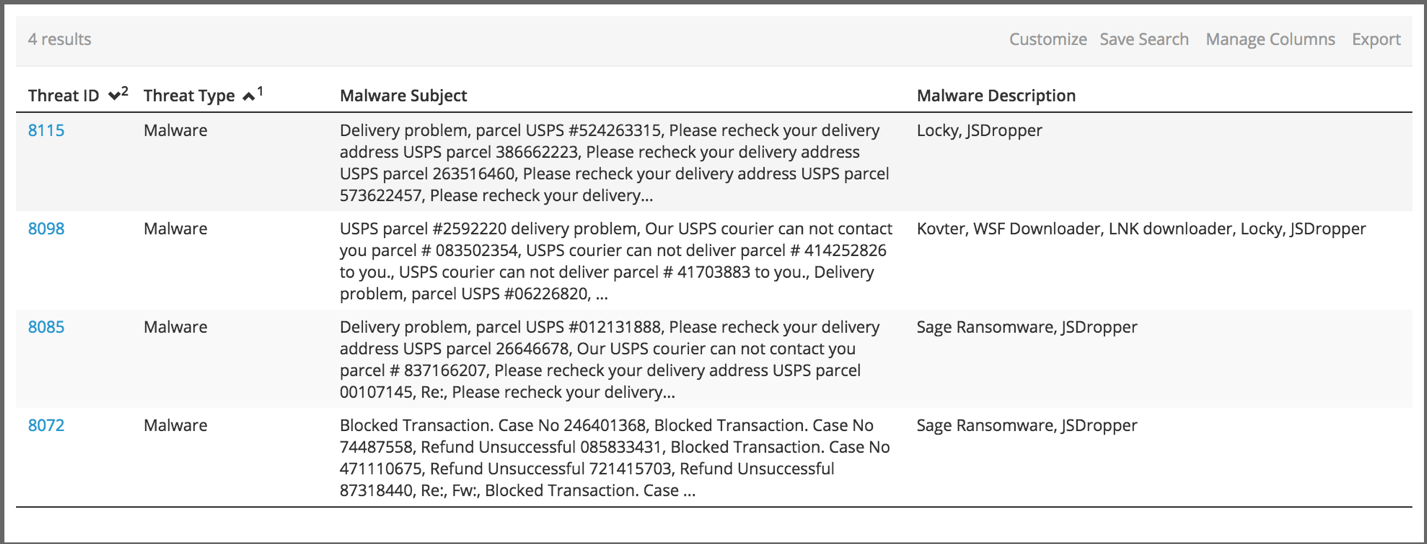
This overlapping infrastructure is a curious link between these two ransomware varieties and serves as a reminder of how malware support and distribution infrastructure is frequently reused. The distribution of Locky and Sage from this singular location also indicates that threat actors are leveraging new ransomware varieties such as Sage while continuing to use the reliable standby tools like Locky. This also provides evidence of the commodity status for ransomware tools like these. The similarity in delivery attributes and infrastructure is ultimately used in the distribution of distinct malware varieties with equal effectiveness for both.
However, these attributes give researchers and security professionals with a few avenues for mitigating these threats. First, the shared infrastructure provides a high-fidelity indicator of compromise that can be preemptively blocked to foil the delivery of multiple ransomware varieties. Secondly, since the qualitative tactics, techniques, and procedures used in the distribution of these ransomware varieties are nearly identical and closely resemble classic phishing narratives easily recognizable to users prepared and empowered to identify and report phishing emails.
Emails based on the threats shown in this blog post are also available as templates in PhishMe Simulator.
Curious to learn more? Download our latest PhishMe Malware Report free today for additional ransomware and phishing research.
Indicators of Compromise:
Sage Ransomware – Threat ID 8072
Artifacts
| document_1.zip | 6e3a603a2baea548a40082fe39ee1e23 |
| doc_details_jOiqRJ.js | 2cc382d13c71e1cfd2be4146fca124ea |
| tGwikyITAZ.js | 94e137db2cae8f0b2c6ed0417c2a3f09 |
| 47542.exe | 6dbd79df861dbe109d2e7db0f01c1fb3 |
| !Recovery_D14.html | fb0087c2b50c9d10061400c7809fca74 |
Watchlist
| Sage payload URL | hxxp://affections.top/ff/55.exe |
| Sage command and control URLs | hxxp://7gie6ffnkrjykggd.er29sl.com/login/ |
| hxxp://7gie6ffnkrjykggd.onion/login/ | |
| hxxp://7gie6ffnkrjykggd.rzunt3u2.com/login/ | |
| Sage payment sites | 7gie6ffnkrjykggd.er29sl.com |
| 7gie6ffnkrjykggd.onion | |
| 7gie6ffnkrjykggd.rzunt3u2.com | |
| mbfce24rgn65bx3g.er29sl.com | |
| mbfce24rgn65bx3g.onion | |
| mbfce24rgn65bx3g.rzunt3u2.com |
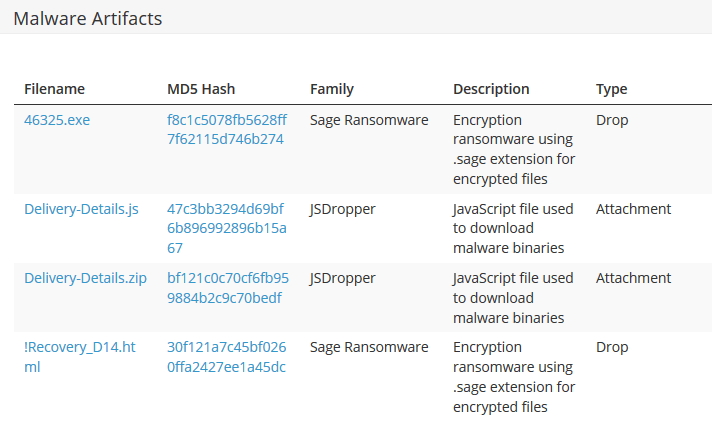
Sage Ransomware – Threat ID 8085
Artifacts
| Delivery-Details.js | 47c3bb3294d69bf6b896992896b15a67 |
| Delivery-Details.zip | bf121c0c70cf6fb959884b2c9c70bedf |
| 46325.exe | f8c1c5078fb5628ff7f62115d746b274 |
| !Recovery_D14.html | 30f121a7c45bf0260ffa2427ee1a45dc |
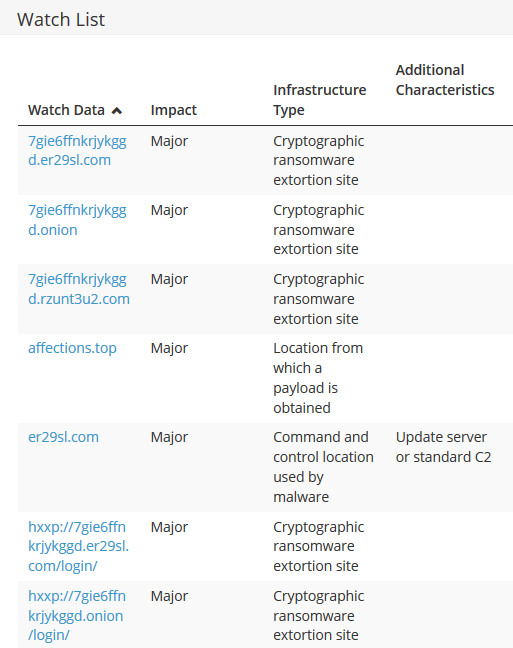
Watchlist
| Sage payload URL | hxxp://affections.top/ff/55.exe |
| Sage command and control URLs | hxxp://7gie6ffnkrjykggd.er29sl.com/login/ |
| hxxp://7gie6ffnkrjykggd.onion/login/ | |
| hxxp://7gie6ffnkrjykggd.rzunt3u2.com/login/ | |
| Sage payment sites | 7gie6ffnkrjykggd.er29sl.com |
| 7gie6ffnkrjykggd.onion | |
| 7gie6ffnkrjykggd.rzunt3u2.com | |
| mbfce24rgn65bx3g.er29sl.com | |
| mbfce24rgn65bx3g.onion | |
| mbfce24rgn65bx3g.rzunt3u2.com |
Locky Ransomware – Threat ID 8115
Artifacts
| Delivery-Details.zip | d60fb8ddb7857a6554e2231ad968df4e |
| Delivery-Details.js | 93e4523dc320167493bee01b11b6fc51 |
| DolXRXWIz.js | c42ca3058385df5555f0197939a24157 |
| 23152.exe | 26f3b9b60aa40c8798767e8be429781b |
| OSIRIS-89e0.htm | 67cc9f88c06539937c20d448797ece99 |
Watchlist
| Locky payload URL | hxxp://affections.top/dd/15.exe |
| Locky command and control URLs | hxxp://194.31.59.5/checkupdate |
| hxxp://88.214.237.45/checkupdate | |
| Locky payment site | g46mbrrzpfszonuk.onion |


