On the 19th of April, the Cofense Phishing Defense Center received an email crafted to appear to be from “Sberbank Russia.” In fact, it was a phishing email containing the Troldesh malware, a variant of Russian Ransomware first seen in mid-2015. The PDC hadn’t seen this variant for quite some time.
Beyond phishing distribution, Troldesh has been used to target thousands of vulnerable WordPress (admin login) sites as tracked by Wordfence researchers in August 2017. During an analysis, we found 1,254 Word Press Administrator login pages in one of the malicious process’s memory.
If successful, it will upload the malicious file onto the website to encrypt the files and extort ransom from the site owner. It allows the victim to interact with the threat actor via email and even grants discounts on ransoms.
Here’s what the email looked like.
The email body was in Russian as demonstrated in figure 1.
 Figure 1
Figure 1
The email seems to be coming from prohorov.s[@]tmmu[.]ru, but our analysis of the email header revealed that the email was actually sent from lightxp[@]ombaksalary[.]pl. The email prompts the user to click on a link that points to sberbank[.]ru/blinov. Inspecting the link reveals it to be a hyperlink, in reality pointing to hxxp://moolianco[.]com/templates/jm_plus/css/?\.
The URL points to a .zip archive containing a malicious JavaScript file.
FILE DETAILS:
Zipped:
File name: vipiska[.]po[.]schetu[.]xls[.]zip
MD5: 713257618e9adf8b4e60e8acdedc546c
SHA1: 69b4aa73f0afdc519fd7a76c1c881a482d97c6c7
SHA256: 966dd1ea42916c37ca463213074edc06da1151bd089477cbc968e3dec6f8ea9b
File Size: 9,230 BytesUnzipped:
FILE name: éd»¿ß¬á »« ßtÑGp[.]xls[.]js
MD5: 86e32a6966e81df198f8f511860f2244
SHA256: ce9090644468fa7627622cea1626644e95c1fa2534ff4044899d03bfa9327837
SHA1: 858f80cf5e44a7d90a42681c9642f720b90281ac
File Size: 22,177 Bytes
Executing the JavaScript file immediately initiates the WScript.exe, which makes a connection to the payload url to download further malware. It reaches out to two payload URLs:
Payload URL:
hxxp://moolianco[.]com/templates/jm_plus/css/1.exe
IP address: 38[.]99[.]139[.]142
(At the time of analysis, this URL was not responding and returned a 404 error.)
hxxp://morcanports[.]com/demo/assets/css/fonts/1.exe
IP address: 103[.]21[.]58[.]231
The downloaded JavaScript file is GEO-IP aware. We were unable to obtain the payload with a Brazilian IP address, but were successful when we switched to a US IP address.
Downloaded Malicious file:
Depending on the system configuration and IP location, one of four files is retrieved:
File name: 1.exe / rad678F8.tmp/ csrss.exe
MD5: 1ab249b24f9c36713b5916c1c961eb41
SHA1: dd939e5cffc4b14dffb758af7d130dae0244d158
SHA256: 9b3af0dd248f86114a0c042e4385649ff294707479a85006a7dd384071213890
File size: 1,449,472 Bytes———————————–
File Name: C0DD6334.exe/csrss.exe
MD5: c1182260e1ba1f930e591a98e75552d9
SHA1: ddfd32c2c5984728f4d60fbc98293aba138e86d1
SHA256: 0df932043d6da40d958284ea8ee065f6269a3babdbb45ff319f2030d0d6fe115
File Size: 1,032,704 Bytes————————————
File Name: 76D18926.exe/csrss.exe
MD5: 8fbe9a961300fb62df587ed708160655
SHA1: d89487914a96dc8e1a6446a2e729d363f9f71d58
SHA256: 9d3bac28e24a997c2d2b3a955b7f0d57494950a0269f1bf31dc45fb1dadcdb84
File Size: 887,808 Bytes———————————
File Name: 508EE6C3.exe
MD5: 42e25d12773ba02c4cf4d4eec77d62eb
SHA1: 11d802c1dbcfc301f25754f08731dd697a7932a1
SHA256: 29a8babbce680179675485b775f2c9ee1c2924afda7236feb31aabf5ddf05c3c
File Size: 1,497,600 Bytes
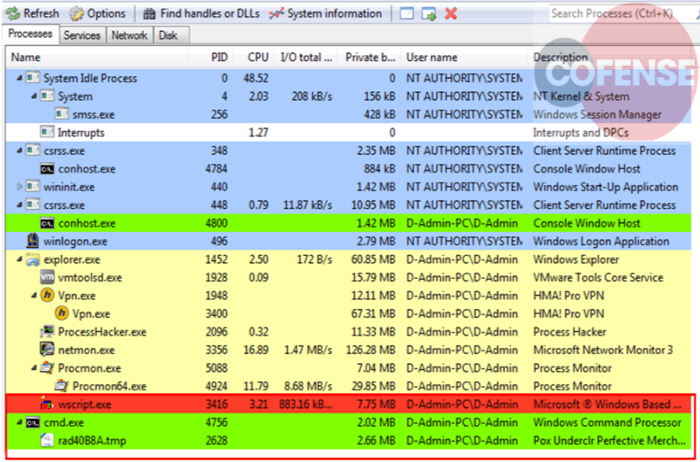
When one of the files above is downloaded and executed, it immediately spawns cmd.exe and initiates the rad678F8.tmp as a child process as shown in figure 2.

Figure 2
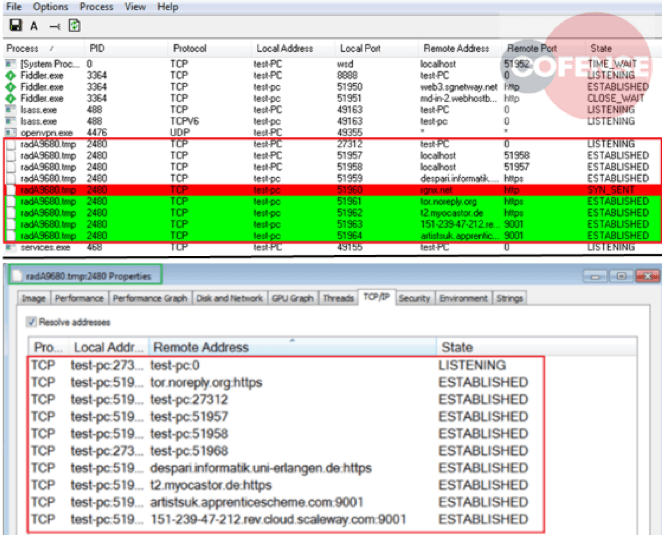
The process starts making connections to various other domains, including domains on the TOR network which can be seen in figure 3.

Figure 3
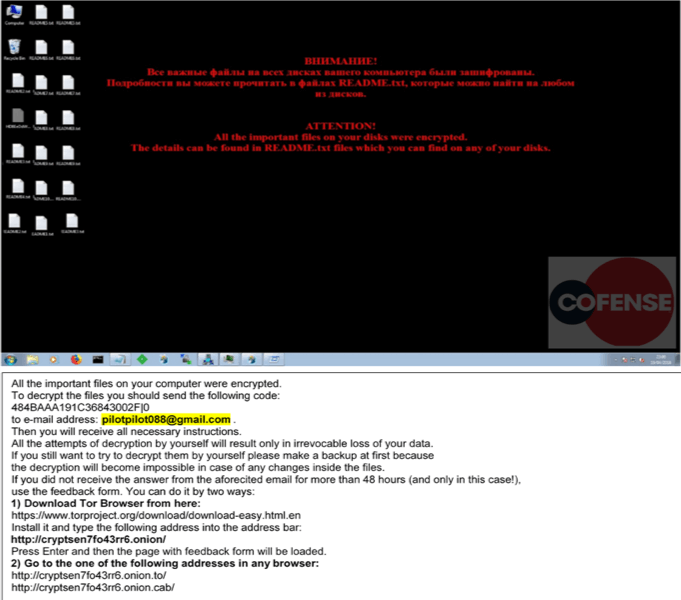
On successful completion of importing the encryption keys and setting up persistence on the victim’s system, the machine is encrypted and presented with the following screen, including several Readme.txt file dropped to the victim’s desktop. The read me file instructs the victim to send an email to pilotpilot088[@]gmail[.]com with the given code for further instruction as demonstrated in figure 4.

Figure 4
Files which are encrypted are renamed with a .CRYPTED000007 file extension.
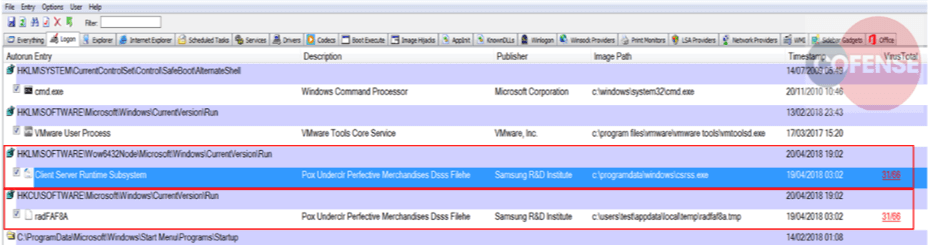
To achieve persistence, the malware changes the registry keys under the following locations of the registry:
HKLMSOFTWAREWow6432NodeMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun (64 Bit System)
HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows CurrentVersionRun (32 Bit System)
Furthermore, it deletes the original JavaScript file from the current location and places the downloaded file under – C:programdatawindowscsrss.exe and C:usersusernameappdatalocaltempradfa8a.tmp as shown in figure 5.
Figure 5
Be on the lookout!
The Troldesh variant appears to be coming back. Businesses and individuals should take precautionary measures to avoid having their machines encrypted and facing ransom demands. Security analysts or operators should be alert for phishing emails that lure users to click on a link or download innocent-looking files to infect their machines. Virtually any type of business, as well as individual website owners, are potential targets.
To see the past year’s malware trends and what to expect now, read the Cofense Malware Review 2018.
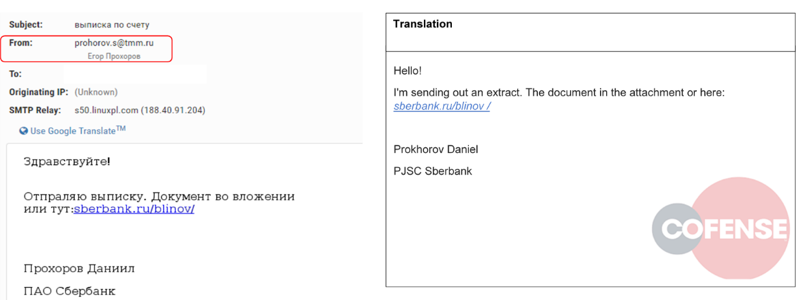 Figure 1
Figure 1