By: Jhon Astronomo, Cofense Phishing Defense Center
Recently, threat actors have been impersonating employees at major companies, such as ADP, a leading global provider of human resources management and payroll processing services.
The Cofense Phishing Defense Center (PDC) recently observed a new phishing campaign imitating ADP, allowing the threat actor to gain access to employee accounts and steal sensitive information. To help employees identify phishing threats and become the first line of defense against threat actors, we broke down this real-life example.
The message claims that the user has violated certain terms and conditions and urges them to log in to resolve the issue, creating a false sense of urgency to trick the user into providing sensitive information.
.png)
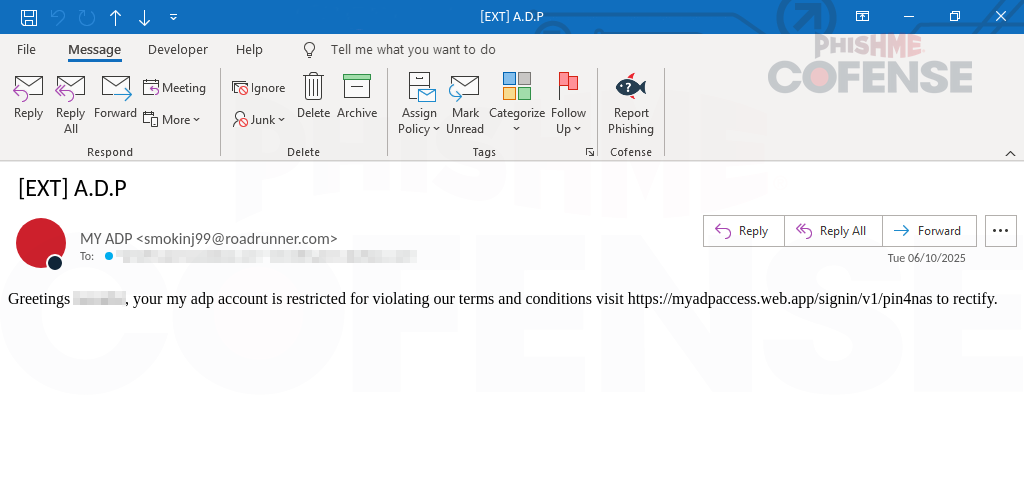
Figure 1: Email Body
At first glance, the email appears to be a simple notification. The email’s display name, shown in Figure 1 as ‘MY ADP’, along with a convincing subject line, seems legitimate. However, the threat actor manipulates the user’s emotions by creating a false sense of urgency, claiming that the user violated certain terms and conditions, and urges them to log in immediately to resolve the issue. This pressure tactic is designed to make the user click the malicious URL without thinking. To make it look more trustworthy, the URL itself may appear familiar to the user because it includes 'ADP' in it, which can lead employees to trust and click without verifying its authenticity.
.png)
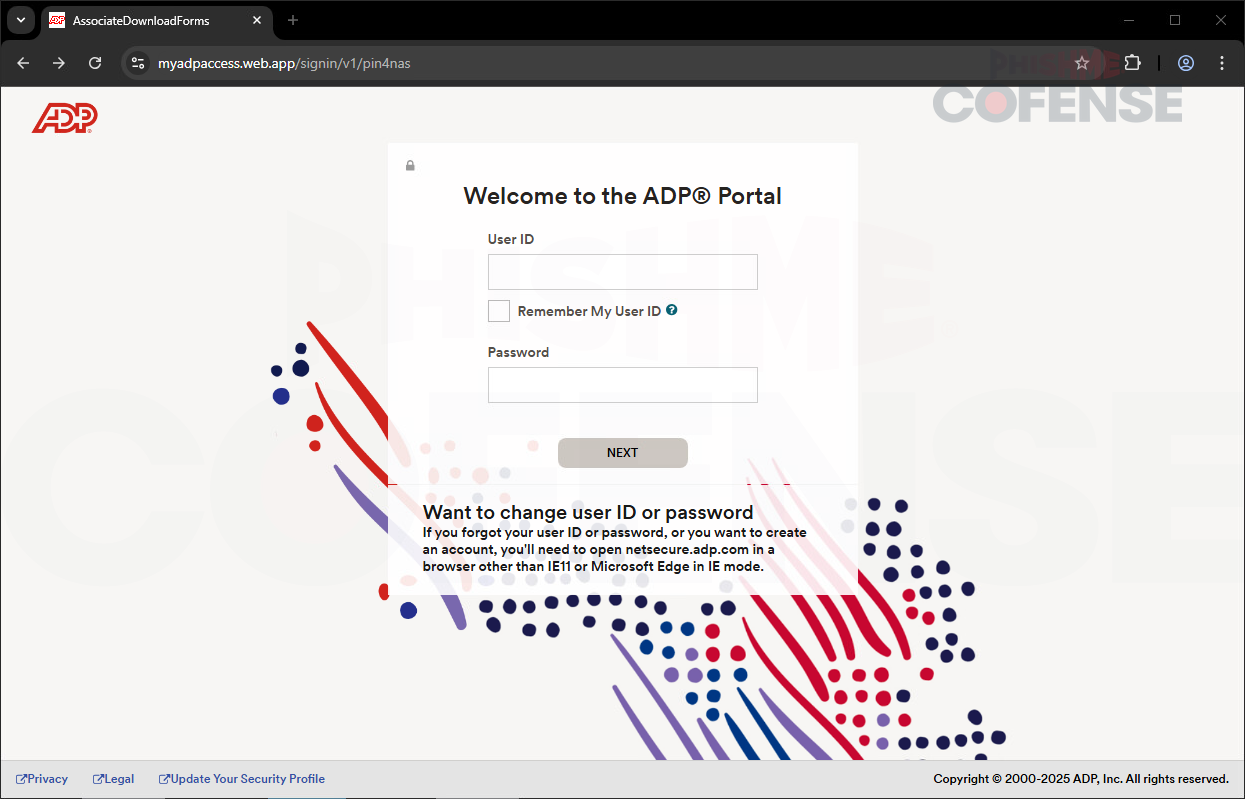
Figure 2: Phishing Page
Once the user clicks the URL, they are redirected to a phishing page shown in Figure 2 that mimics the legitimate ADP website, making it appear authentic to the user’s eyes. However, when looking closely at the URL (hxxps://myadpaccess[.]web[.]app/signin/v1/pin4nas), it is an obvious indicator that this is a counterfeit or phishing URL. After entering the user ID and password, the user will be redirected to the phishing page shown in Figure 3.
.png)
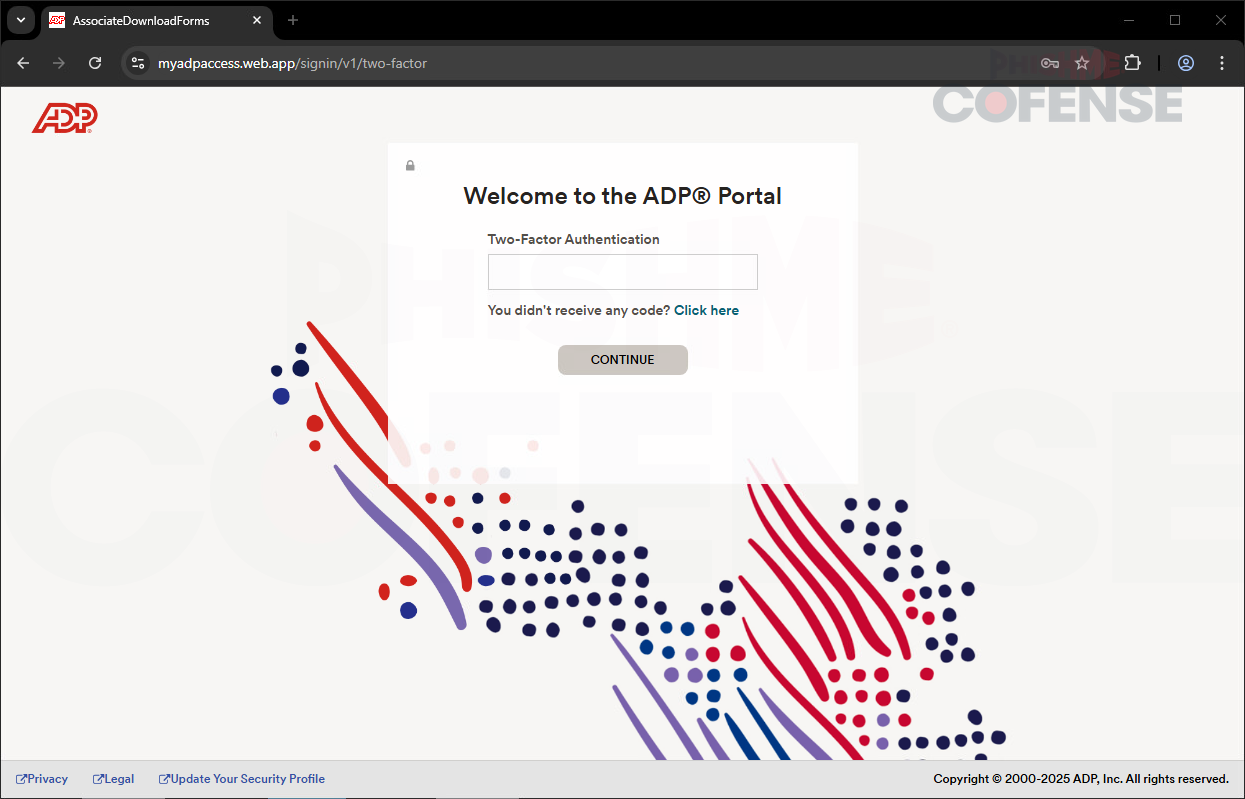
Figure 3: 2FA Theft Page
On this part of the phishing page, which closely resembles an ADP login page, the threat actor will ask if the user received a code for two-factor authentication to create a false sense of security. Of course, the user will not receive any code because it is a fake phishing page. In the urgency to resolve the issue, the user might click the ‘Click here’ hyperlink on the page. This is a tactic used by the threat actor to manipulate user emotions. After clicking the hyperlink, the user will be redirected to the page shown in Figure 4.
.png)
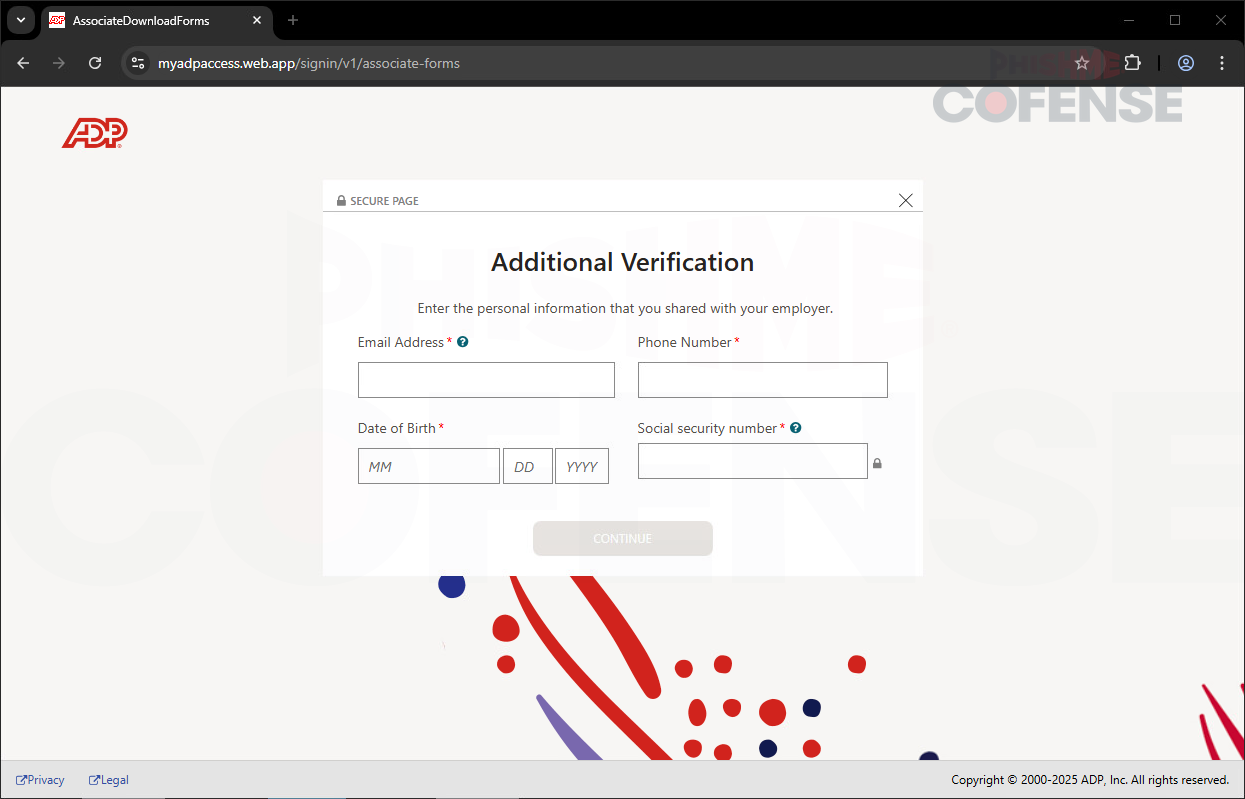
Figure 4: Additional Verification Phishing Page
This is the part where the threat actor asks for additional verification, mimicking the legitimate ADP page to make it appear as though they are confirming the user identity. They will request personal information such as the user’s email address, phone number, date of birth, and Social Security number. After the information is submitted, it will be exfiltrated to a web server hosted by the threat actor, giving them full access to the victim’s account and personal data. With these details, they can easily log in to the user account and access sensitive information such as pay stubs, W-2 forms, and 401(k) accounts.
This phishing campaign showcases how threat actors manipulate people psychologically. They exploit emotions by creating scenarios that appear urgent and risky for both the company and the individual. These attackers have evolved by closely mimicking legitimate websites and consistently creating a false sense of urgency to trick users into entering sensitive information. This highlights the importance of email security. It is crucial to encourage all employees and users to learn the proper steps to take when receiving suspicious emails. At Cofense, our PDC team uses a powerful combination of human intelligence and advanced technology to detect malicious email attacks. Our goal is to ensure customers always feel safe and protected. Schedule a demo with our team of experts today to learn more.