By Alan Rainer and Max Gannon
On the malware front, the summer of 2019 was quiet and steady-state. But the end of Q3 saw the infamous Emotet resurface, presaging a malware uptick in Q4. Read all about it in the Cofense Q3 2019 Malware Trends Report.
Maintaining a relative lull when Emotet suspended activity, threat actors in Q3 stuck to tried-and-true practices of intrusion. Phishing emails containing keyloggers (namely ‘Agent Tesla’) slightly rose in popularity, while information stealers like Loki Bot fell. Threat actors continue to seek the easiest, most efficient way of infiltrating users. Agent Tesla, for example, offers customer support and a web interface to develop and manage the keylogger. Similarly, cybercriminals continue to capitalize on known and patched vulnerabilities to deliver malware through phishing campaigns.
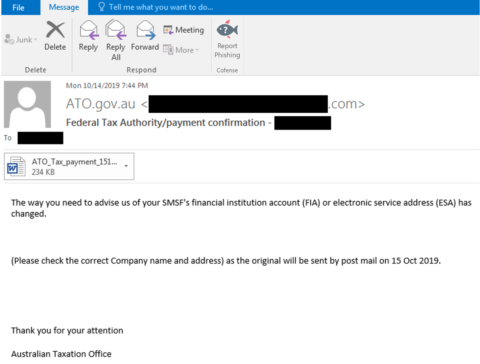
When Emotet resurfaced towards the end of Q3, this significant malware player wasted no time in compromising email chains or tricking users with convincing templates. As such, CofenseTM expects Q4 to show more malware activity.
Figure 1: Emotet Phishing Email Sample
Our Q3 report outlines these trends, alongside statistics, breakdowns of specific campaigns, and insights on what to expect in Q4, all of which you can use to defend your organization. Cofense IntelligenceTM provides phishing campaign updates throughout the year, which include the Strategic Analysis (a comprehensive threat report) and Executive Phishing Summary (a bi-weekly trend synopsis) communiqués.
All third-party trademarks referenced by Cofense whether in logo form, name form or product form, or otherwise, remain the property of their respective holders, and use of these trademarks in no way indicates any relationship between Cofense and the holders of the trademarks. Any observations contained in this blog regarding circumvention of end point protections are based on observations at a point in time based on a specific set of system configurations. Subsequent updates or different configurations may be effective at stopping these or similar threats.