Real Phishing Email Examples & Threats: Phishing Database
Cyber threats are ever evolving, meaning that you need to stay vigilant to keep your business safe from attack. Phishing emails are still one of the most common ways for criminals to target companies and steal data, so it’s essential that your employees recognize them as soon as possible.
Understanding the potential danger posed by these malicious emails is essential if you want to protect your business. Some of the top SEGs in the world missed all of these phishing attacks below. Learn more about real phishing email examples and the serious threats they pose!
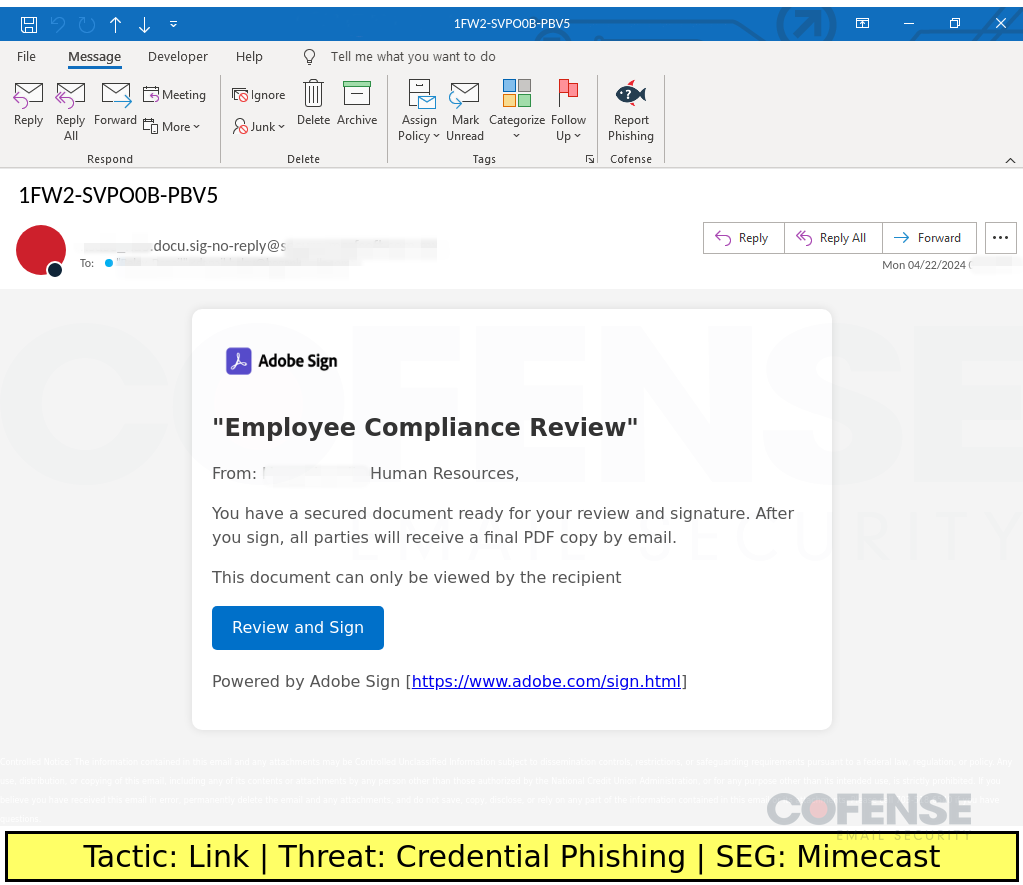
Mimecast
Type: Credential Phishing
Posted On: 04/23/2024
Tactic: Link
Theme: Notification
Phishing Email Example Description:
Notification-themed emails found in environments protected by Mimecast deliver Credential Phishing via an embedded link.
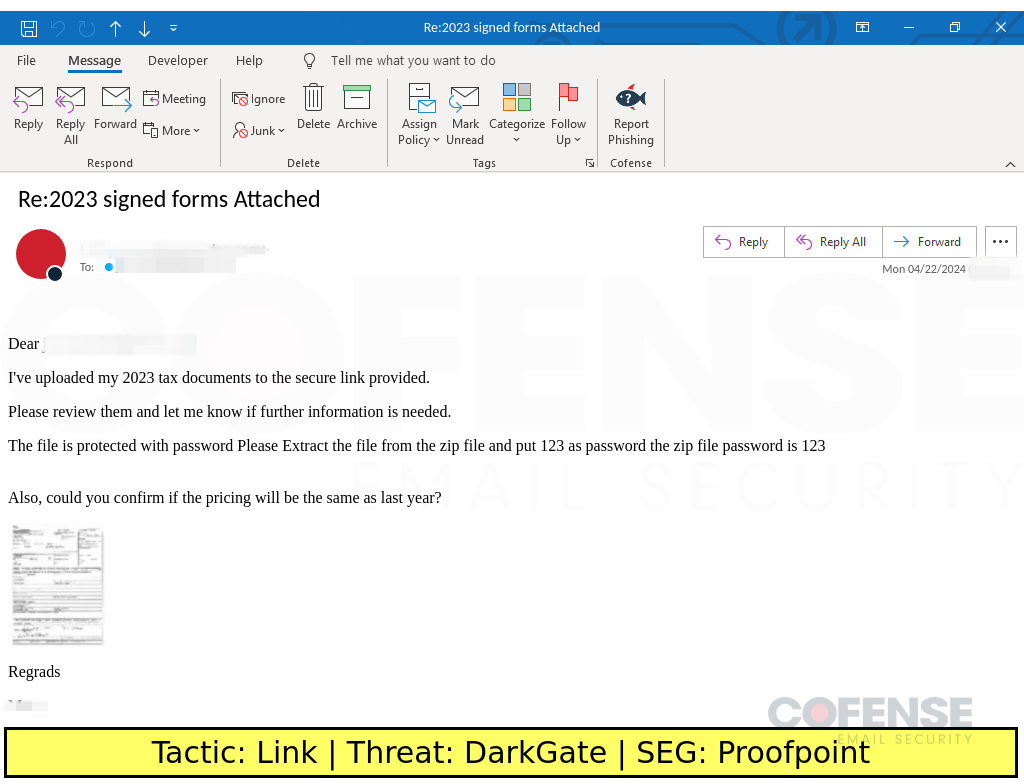
Proofpoint
Type: DarkGate
Posted On: 04/23/2024
Tactic: Link
Theme: Taxes
Phishing Email Example Description:
Taxes-themed emails found in environments protected by Proofpoint deliver DarkGate via an embedded link. The embedded link downloads a password protected ZIP archive that contains a DarkGate executable and DLL file.
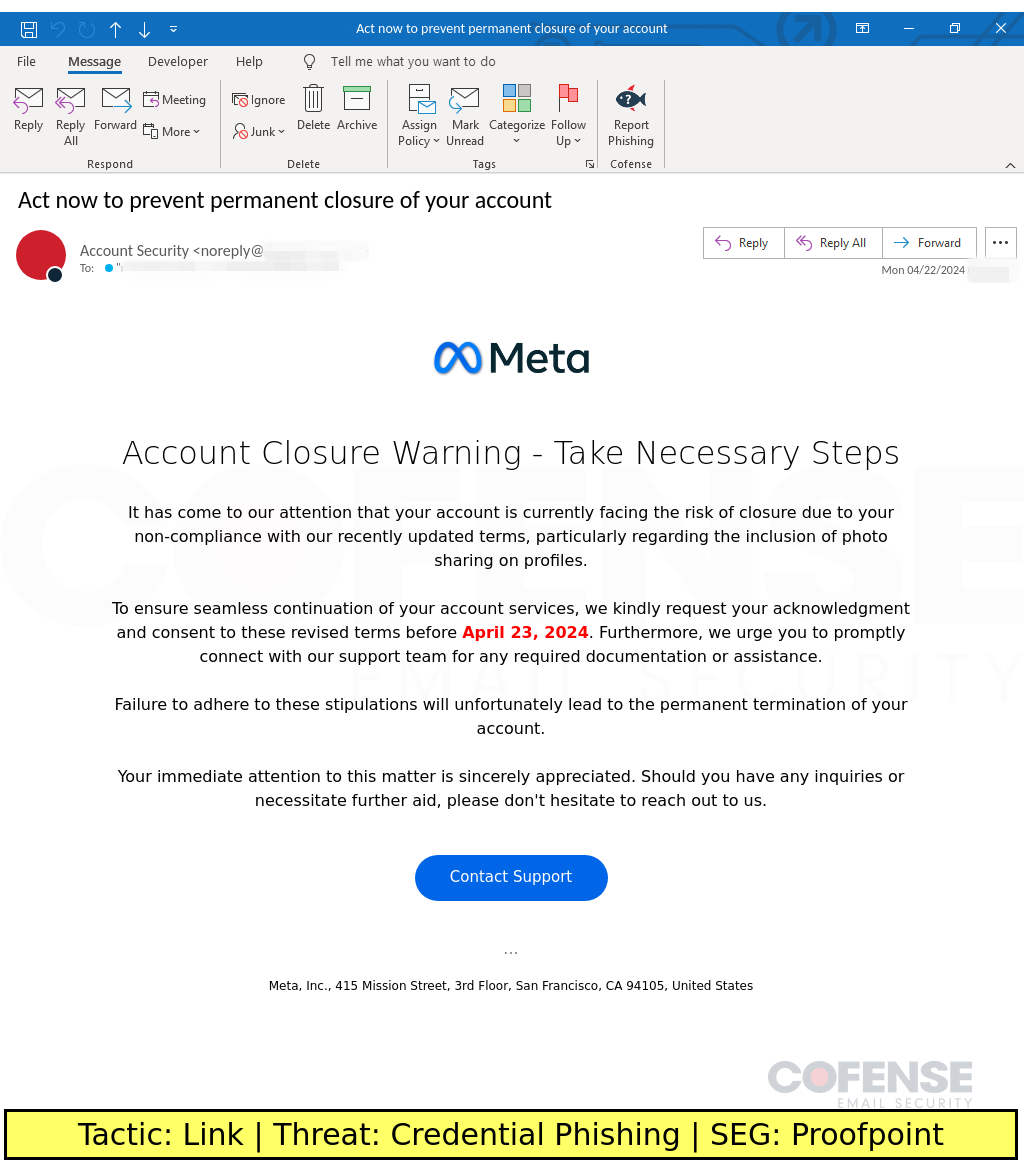
Proofpoint
Type: Credential Phishing
Posted On: 04/22/2024
Tactic: Link
Theme: Meta
Phishing Email Example Description:
Meta-spoofing emails found in environments protected by Proofpoint deliver Credential Phishing via an embedded link.
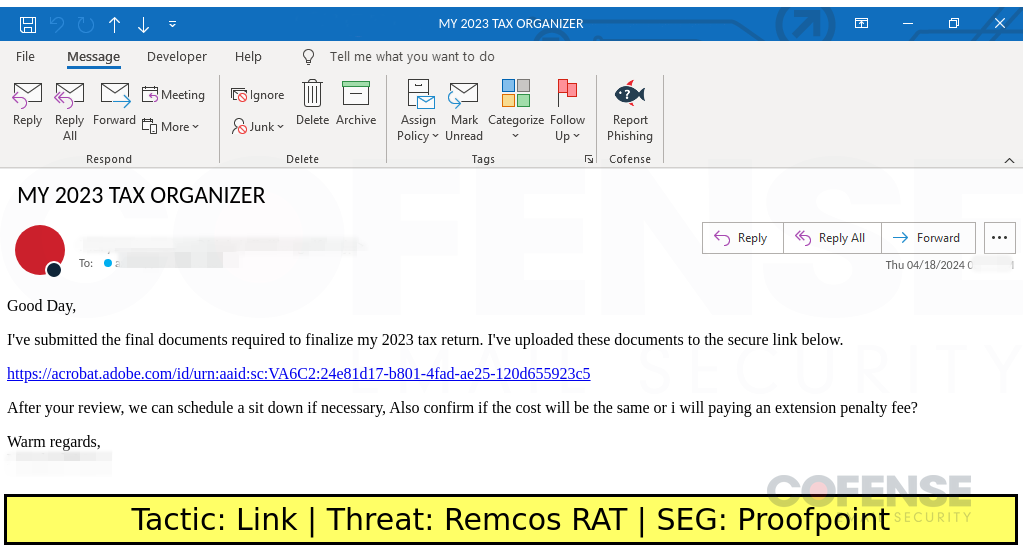
Proofpoint
Type: Remcos RAT
Posted On: 04/19/2024
Tactic: Link
Theme: Taxes
Phishing Email Example Description:
Taxes-themed emails found in environments protected by Proofpoint deliver Remcos RAT via an embedded URL.
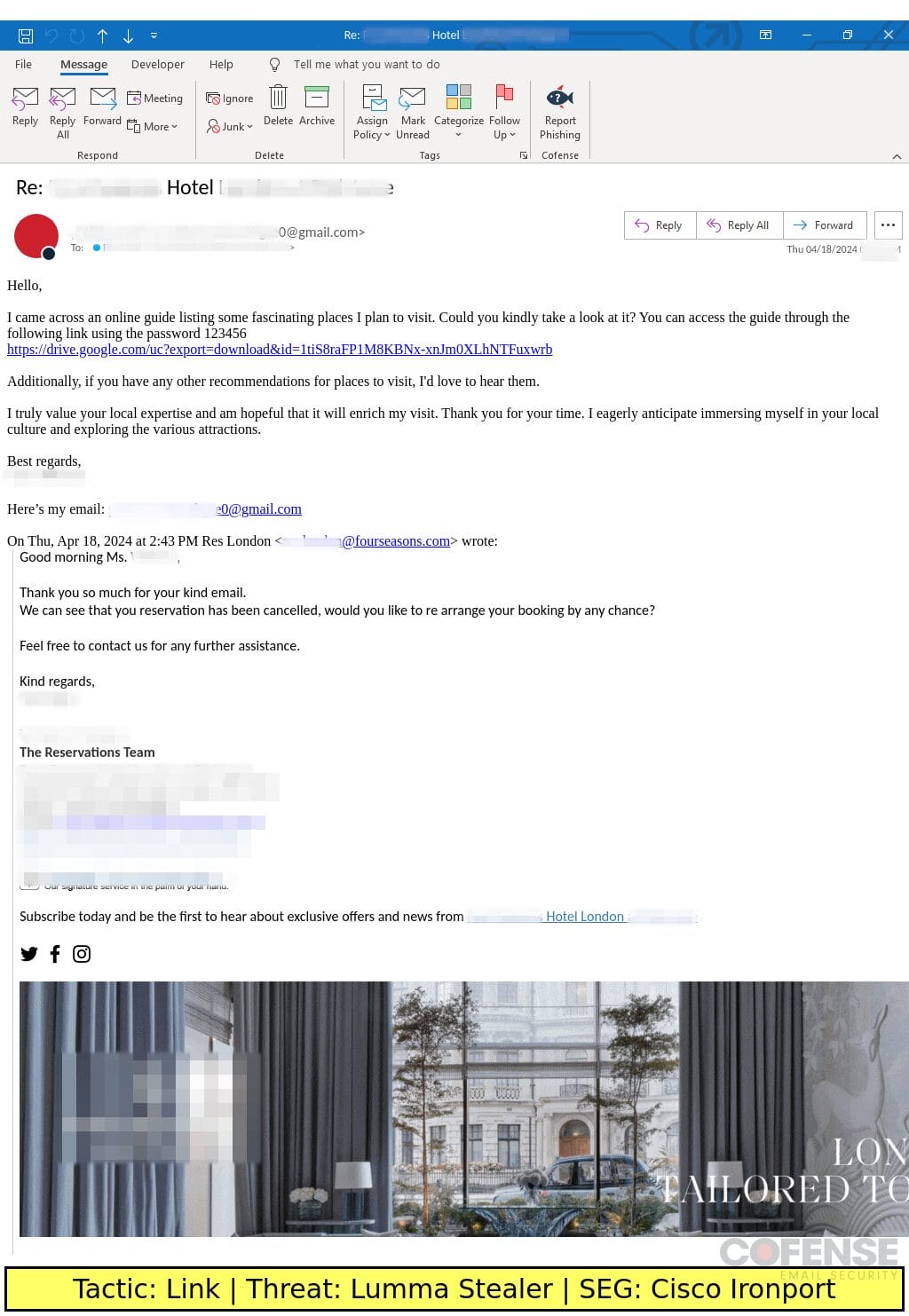
Cisco ironport
Type: Lumma Stealer
Posted On: 04/18/2024
Tactic: Link
Theme: Travel Assistance
Phishing Email Example Description:
Travel Assistance-themed emails found in environments protected by Cisco Ironport deliver a password protected archive containing an artificially inflated sample of Lumma Stealer.
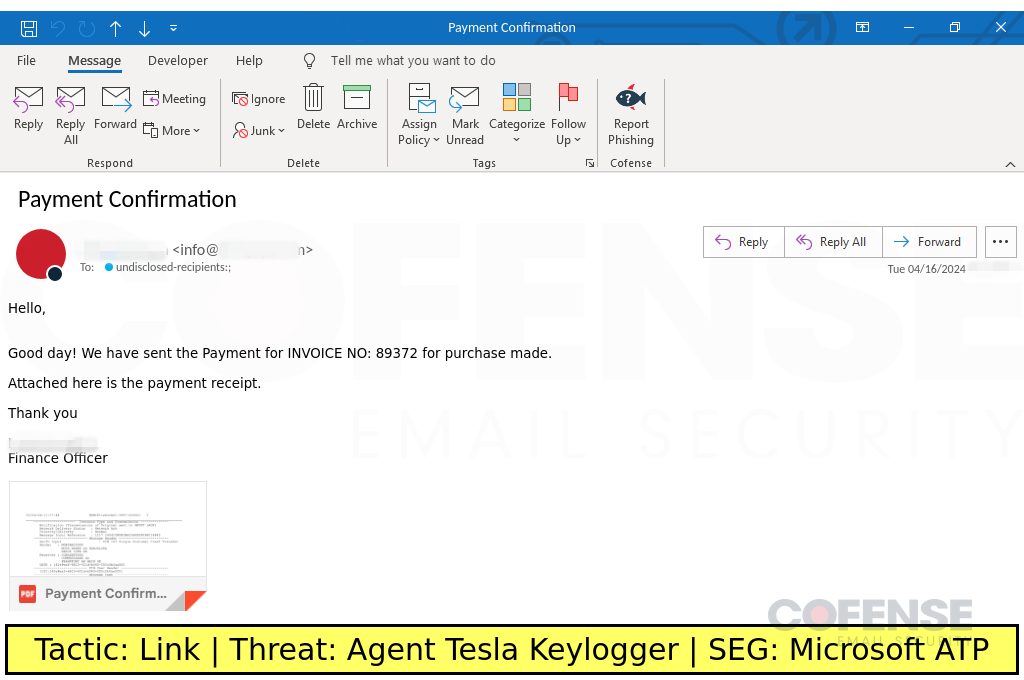
Microsoft ATP
Type: Agent Tesla Keylogger
Posted On: 04/17/2024
Tactic: Link
Theme: Finance
Phishing Email Example Description:
Finance-themed emails found in environments protected by Microsoft ATP deliver an archive containing an artificially inflated sample of Agent Tesla Keylogger via an embedded URL.
Phishing Email Examples FAQs
Phishing emails are malicious email messages that attempt to trick victims into disclosing sensitive personal information, such as credit card numbers, passwords, and Social Security Numbers. These types of emails commonly feature a sense of urgency or alarm that encourages the recipient to act immediately. Below are some examples of phishing email scams:
Fake invoice notifications: Sent with phishing email subject lines like “We have an unpaid invoice for you” or “Your payment is overdue”
Job offers scams: Recipients receive bogus emails from fake companies offering high paying jobs with no experience necessary.
Fake charity requests: This type of phishing email asks the recipient for donations in order to help those affected by natural disasters or other tragedies.
Fake software updates: Victims receive a notification telling them their software needs updating due to security issues and asking them to click on links provided in order download new version. The link then redirects users onto malicious websites containing ransomware.
To warn staff about phishing email examples, first provide a definition of phishing. Explain that it involves messages sent via email, text message, social media posts, or other forms of electronic communication designed to deceive recipients into revealing personal details such as passwords and credit card numbers or downloading malicious software.
Explain how users can spot a potential malicious message before responding to them. Inform them of signs like misspelled words (e.g., ‘shipping’ instead of ‘shippping‘), generic salutations (i.e., “Dear Customer” rather than using their name), out-of-the-ordinary requests (like wiring money), hyperlinks without proper context and unrecognizable logos among others that could indicate an illegitimate source attempting fraudulence.
Advise employees about measures they should take in case they receive any suspicious emails. Encourage them to contact their IT department.
A phishing attack is when a fraudster sends an email to trick the recipient. The idea is to persuade the target into giving up sensitive information, for instance, your corporate network credentials, or perhaps to authorize some type of financial transaction. The vast majority of data breaches against businesses today begin as phishing attacks.
Just a couple of famous phishing examples:
The infamous Target breach back in 2013 started with a phishing email that gave attackers a foothold in Target’s business systems for further attacks.
Phishing appeared prominently in the Mueller Report on the 2016 presidential election hacking.
Some quick phishing statistics:
- Over 55% organizations experienced a successful phish last year.
- $12 billion is the 5-year global cost of just one type of phishing attack, business email compromise (BEC).
- The average phishing attack costs a mid-sized business $3.86 million.
Our database has thousands of phishing examples, but most fit into one of these 3 categories:
Phishing Emails with Malicious Links: Sometimes a phishing attack is simply an email with an embedded link. When you click, you either unknowingly activate malware or are directed to a webpage that looks perfectly legitimate but is designed to harvest your information.
Phishing Attacks with Malicious Attachments: Phishing attackers often send emails with attachments containing malware. When you click, look out. Many times phishing attackers use popular document types such as Microsoft Word or Excel or even Adobe PDFs. They take advantage of the trust people place in popular business tools.
Business Email Compromise (BEC): BEC emails, also known as CEO Fraud, typically don’t use malware but simply try to manipulate the target into sending money. Traditionally, BEC phishing attacks try to get employees in the finance department to authorize wire transfers, for instance, to a “vendor” or “partner.” This kind of attack often uses ‘CEO fraud phishing’ where attackers pretend to be the CEO or CFO to spur quick action.
Phishing email examples provide highly useful intelligence that helps security teams better pinpoint attacker methods and tactics. They help protect businesses from malware-bearing phish. Because attacker campaigns change quickly, real-world phishing email examples are a central component of comprehensive security. Phishing attack examples reveal the latest threat actor maneuvers as they are being launched.
All third-party trademarks referenced by Cofense whether in logo form, name form or product form, or otherwise, remain the property of their respective holders, and use of these trademarks in no way indicates any relationship between Cofense and the holders of the trademarks.